Dive Brief:
- Amazon reduced its scope 2 emissions, or indirect emissions from purchased electricity, by 11% year over year in 2023, representing 2.79 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, according to its 2023 Sustainability Report released July 10.
- The company cut its absolute carbon emissions 3% year over year in 2023, reducing its carbon intensity by 13% in that time. The company attributed the decrease in scope 2 emissions to its increased use of renewable energy-sourced electricity and its purchase of additional environmental attributes such as renewable energy credits.
- Improving energy efficiency and transitioning to carbon-free energy are the two most important ways it lowers electricity-related carbon emissions, Amazon said. The company noted that scaling renewable energy use involves implementing on-site renewable energy, such as rooftop solar installations on its buildings; ramping up its use of refrigerants with low global warming potential; and utilizing alternative fuels as backup power sources and for data center cooling.
Dive Insight:
Amazon’s overall carbon emissions declined to 68.82 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent in 2023, per the report. Its direct operating emissions, comprising emissions from fossil fuels and refrigerants, rose 7% year over year to 14.27 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent, driven by an 8% year-over-year increase in fossil fuel emissions and offset by a 25% reduction in refrigerant emissions, the report says.
The construction, operation and decommissioning of Amazon’s building portfolio accounted for one-fifth of its total carbon emissions, the company says. To reduce carbon emissions from building operations, including those from HVAC and lighting systems, Amazon says it is focusing on improving data collection practices.
Making its buildings more energy efficient and reducing their carbon emissions must start “with collecting robust, accurate, timely, and meaningful data to identify opportunities for improvement,” the organization said. Amazon utilizes its enterprise building management system to track energy efficiency in existing sites, deploying the EBMS in more than 1,200 facilities by the end of 2023, according to the report.
The standardized EBMS platform manages facility energy use and controls building systems to minimize associated carbon emissions, using thousands of sensors in many buildings to monitor water use, air flow, temperature and other environmental factors that can help the company further improve and optimize its designs, Amazon said.
Amazon said it can increase energy efficiency by implementing lighting and EBMS retrofits, alongside rooftop heating, ventilation air conditioning unit replacements. Lighting retrofits alone have saved 1.23 billion megawatt hours of energy and avoided more than 873,000 metric tons of CO2 dioxide equivalent from 2017 to 2023, the company says. These retrofits involved converting all non-LED lamps to high-efficiency LED fixtures with dimming controls, per its report.
The company says it brought 50 on-site solar energy systems online for a total capacity of 58 MW in 2023, bringing its total number of global rooftop solar projects to 270. These systems are estimated to generate 123,000 MWh annually and avoid the equivalent of approximately 47,400 metric tons of CO2 equivalent each year, compared with non-renewable electricity sources, per the report.
To minimize energy and water consumption in its operations, including in data centers, the company notes that it is increasing its use of free-air cooling systems that cool servers with outside air, avoiding the need for energy-intensive compressor-based cooling systems for a large portion of the year.
“Even during peak summer temperatures, data centers can utilize direct evaporative cooling, a process that uses water to cool the air and remove heat from servers,” it says in the report.
The company said it is focused on creating more energy efficient chips. In 2023 the company designed Inferentia2, a chip that offers “the highest performance at the lowest cost per watt” and is 50% more energy-efficient, with a potential to cut costs by up to 40% against comparable Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud chips, it said.
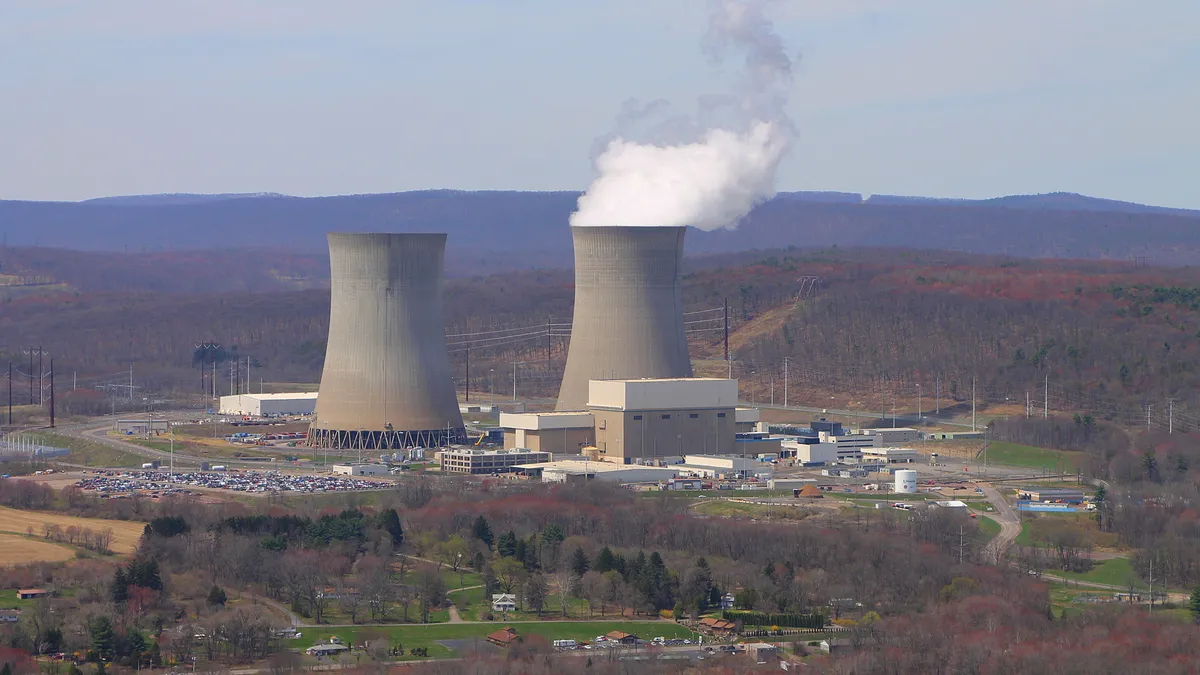
In early 2023, Amazon also purchased a nuclear-powered data center in Pennsylvania that is directly powered by the Susquehanna Steam Electric Station. The company notes that it believes nuclear energy is a strong option with a track record of providing a constant source of reliable power and that its investment in nuclear power is part of its broader efforts to decarbonize its business.
The company said it has also adopted a multi-pronged approach to decarbonize its fleet. These strategies include scaling the use of electric vehicles and micro-mobility solutions, including charging infrastructure and electric trucks and delivery vehicles, and investing in infrastructure for charging electric heavy goods vehicles. In 2023, the company grew its U.S. fleet of Rivian electric delivery vans to 11,800, from 2,600 in 2022.
In addition to its direct and electricity-related emissions, Amazon’s scope 3, indirect source emissions declined 5% year over year to 51.76 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent in 2023, attributable in part to a 13% year-over-year reduction to 8.95 million metric tons in emissions from capital goods, which include building construction, servers and other hardware, equipment and vehicles, according to the report.